Male Yeast Infections: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Fast Treatments

Yeast infections aren’t exclusive to women; men can also develop them. Male yeast infections are caused by the overgrowth of Candida albicans, a naturally occurring fungus in the human body. Though more common in women, men are not immune to this condition. These infections typically affect the genital area but can occur in other parts of the body, especially in moist and warm environments.
What Causes Male Yeast Infections?
Several factors can increase the likelihood of a yeast infection in men:
Unprotected Sexual Contact
- Yeast infections are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), but men can develop them after sexual contact with a partner who has a yeast infection.
Poor Hygiene
- Insufficient cleaning of the genital area or leaving it moist for extended periods can promote yeast growth.
Uncircumcised Men
- The foreskin can trap moisture and provide an ideal environment for yeast to thrive.
Diabetes
- High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of yeast infections as sugar promotes fungal growth.
Weakened Immune System
- Conditions such as HIV, cancer treatments, or prolonged use of medications like steroids can lower immunity and make infections more likely.
Use of Antibiotics
- Antibiotics disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the body, allowing yeast to overgrow.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Male Yeast Infection
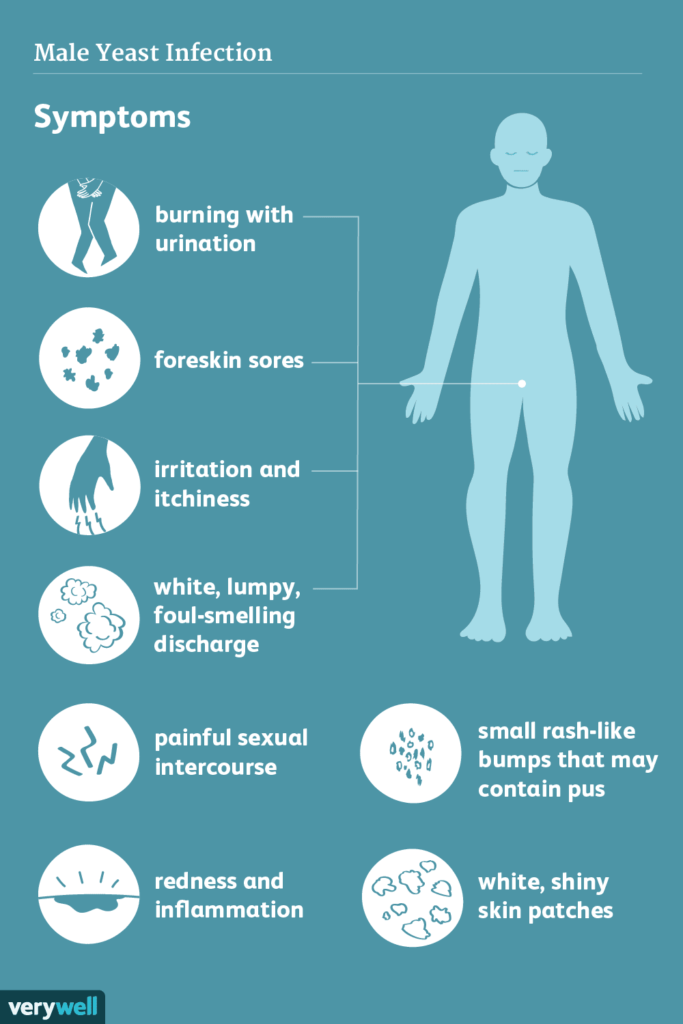
Symptoms of a male yeast infection often appear on the penis but can also occur elsewhere. Common symptoms include:
- Genital itchiness
- Redness and swelling of the foreskin or head of the penis (balanitis)
- Trouble pulling back the foreskin
- Cracking or bleeding of the foreskin
- White, foul-smelling discharge
- Small rash-like bumps on the penis, sometimes pus-filled
- Pain during urination
- Pain during sex
When balanitis in uncircumcised men is severe, it can lead to the inability to retract the foreskin (phimosis) or the inability to return the foreskin to its normal position (paraphimosis). Paraphimosis is a medical emergency.
Treatment of Male Yeast Infections
Male yeast infections are mainly treated with antifungal drugs applied directly to the skin of the penis. Depending on the severity, an over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription antifungal cream, lotion, or ointment may be recommended. Some may also need to take an antifungal by mouth to fully kill the fungus.
Among the topical antifungals your doctor may recommend are:
- Desenex (miconazole)
- Lotrimin (clotrimazole)
- Selezen (imidazole)
These medications are applied to the affected skin and can usually resolve an infection within seven to 21 days. If these topical antifungals fail to provide relief or your immune system is compromised, your doctor may prescribe an oral antifungal like Diflucan (fluconazole) for seven to 14 days.
To protect others and give your body a chance to heal, avoid sex until the infection is fully resolved. Having sex with a penile yeast infection may not only transmit the fungus to the vagina but to the anus as well.
Preventing Male Yeast Infections
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of yeast infections in men. Maintaining a healthy weight is one way to reduce the risk.
Diabetes is also linked to penile yeast infections. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels are thought to contribute to the overgrowth of yeast. Preventing diabetes and maintaining good blood sugar control if you have diabetes may help reduce the risk of a penile yeast infection.
Using condoms during sex may help prevent penile yeast infections.
Proper hygiene can also help. This includes washing the penis and foreskin thoroughly with warm water and drying the area completely. Avoid irritating soaps, deodorizers, or perfumed lotions. Wear breathable underwear to keep the penis and groin dry.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
It helps to see a doctor if the symptoms are severe or unusual. If the problem is related to a tight foreskin, circumcision may be recommended.
If you decide to self-treat and OTC treatments don’t work, or the yeast infection recurs, it’s important to see a doctor for an evaluation.
Key Takeaways
Male yeast infections, also known as penile thrush or penile candidiasis, are caused by the overgrowth of the fungus Candida albicans. This can lead to redness, swelling, and itching of the penis and foreskin, as well as a foul-smelling discharge and small rash-like bumps. Uncircumcised men are more commonly affected.
Male yeast infections are usually treated with topical antifungals, though severe cases may require an oral antifungal. Good hygiene, weight loss, and the consistent use of condoms can help reduce your risk of penile thrush.https://blackairreviews.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-vaginal-yeast-infections-causes-symptoms-and-effective-treatmen
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and should not substitute professional medical advice. For specific concerns about your health, consult a qualified healthcare provider.




The text is in English. Here’s a comment in English:
Mangoes truly are a summer staple, offering both refreshment and versatility in the kitchen. Mocktails sound like the perfect way to enjoy a flavorful drink without the alcohol, especially during hot weather. The mention of traditional Indian drinks like Kanji and cucumber raita highlights how different cultures have unique ways to stay cool. It’s fascinating how food and drinks can be both hydrating and delicious. What other traditional summer drinks or dishes from around the world could be worth trying?
JPGtoPNGHero.com is a free, online converter crafted to turn JPG files into PNG images with ease. Whether you’re preparing icons for a mobile app or converting family photos for a digital scrapbook, the process is straightforward: upload, wait a moment, and download. The server-side engine preserves image quality, ensuring sharpness and accurate color reproduction. A visible progress indicator tracks each file’s status in real time. Need to convert a whole folder of images? Batch conversion handles multiple JPGs at once, streamlining your workflow. Since the converter works entirely in a browser, it’s compatible with Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS—no installations required. Privacy is built in: all uploads are automatically deleted shortly after processing, and no user data is stored on the server. The site remains ad-free, requires no user account, and imposes no conversion limits. Whether you’re a digital artist, social media manager, or just someone who needs to change image formats, JPGtoPNGHero.com offers a fast, reliable, and hassle-free experience.
JPGtoPNGHero
Hello there, You’ve done a great job. I will definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m confident they will be benefited from this website.
http://billiard-classic.com.ua/chomu-desheve-sklo-far-ne-zavzhdy-pohanyj-vybir.html
Thank you for any other informative web site. The place else could I get that type of info written in such a perfect approach? I have a venture that I am simply now running on, and I have been at the look out for such info.
https://igrotech.com.ua/yak-ne-kupyty-stekla-na-far-vid-inshoyi-modeli.html
температура воды в хургаде в апреле
Hi, this weekend is fastidious for me, for the reason that this time i am reading this wonderful educational article here at my house.
https://amato.com.ua/svitlodiodni-lampy-ta-pdr-shcho-dozvoleno.html
Great website you have here but I was curious about if you knew of any message boards that cover the same topics talked about here? I’d really love to be a part of community where I can get opinions from other experienced individuals that share the same interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know. Thanks!
https://cosmeticdentistryaustin.com/led-linzy-v-fary-shcho-potribno-znaty-pered-pokupk.html
download steam desktop authenticator it is a desktop emulator of the Steam authentication mobile application. This desktop application allows users to manage their two-factor authentication easily, ensuring that only you can access your account.
занятия кайтсерфинг
Hey! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest writing a blog article or vice-versa? My website discusses a lot of the same topics as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to shoot me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
Want excitement? You will find it on ck222 casino.
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальныеInsights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Подробнее – https://nakroklinikatest.ru/
Just desire to say your article is as astonishing. The clarity in your post is simply nice and i could assume you are an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the enjoyable work.
Dismemberment
Hello there, You’ve done a fantastic job. I’ll certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m confident they will be benefited from this web site.
Dismemberment
Календарь огородника http://inforigin.ru/ .
Календарь стрижек istoriamashin.ru .
Гороскоп https://topoland.ru .
dragonslots dragonslots .
pokies net 101 pokies net 101 .
The Pokies net Australia https://www.pokies106.com .
айфлоу сайт https://www.citadel-trade.ru .
карниз с приводом для штор elektrokarniz90.ru .
рулонные шторы на балконные окна http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom15.ru .
изготовление металлических значков на заказ http://www.znacki-na-zakaz.ru .
прогноз матчей по футболу https://www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol1.ru .
прогноз на футбольный матч прогноз на футбольный матч .
прогнозы на периоды в хоккее https://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej.ru .
mostbet hesab yaratmaq https://mostbet3041.ru
iphone санкт петербург https://kupit-ajfon-cs.ru/ .
айфон про +в кредит айфон про +в кредит .
mostbet qanunidirmi https://www.mostbet4048.ru
карнизы для штор купить в москве http://elektrokarnizy10.ru .
1win token to usd http://1win3028.com/
apk 1win apk 1win .
1win bonus https://1win3027.com/